Manage Deals and Pipelines Effectively for Business Growth
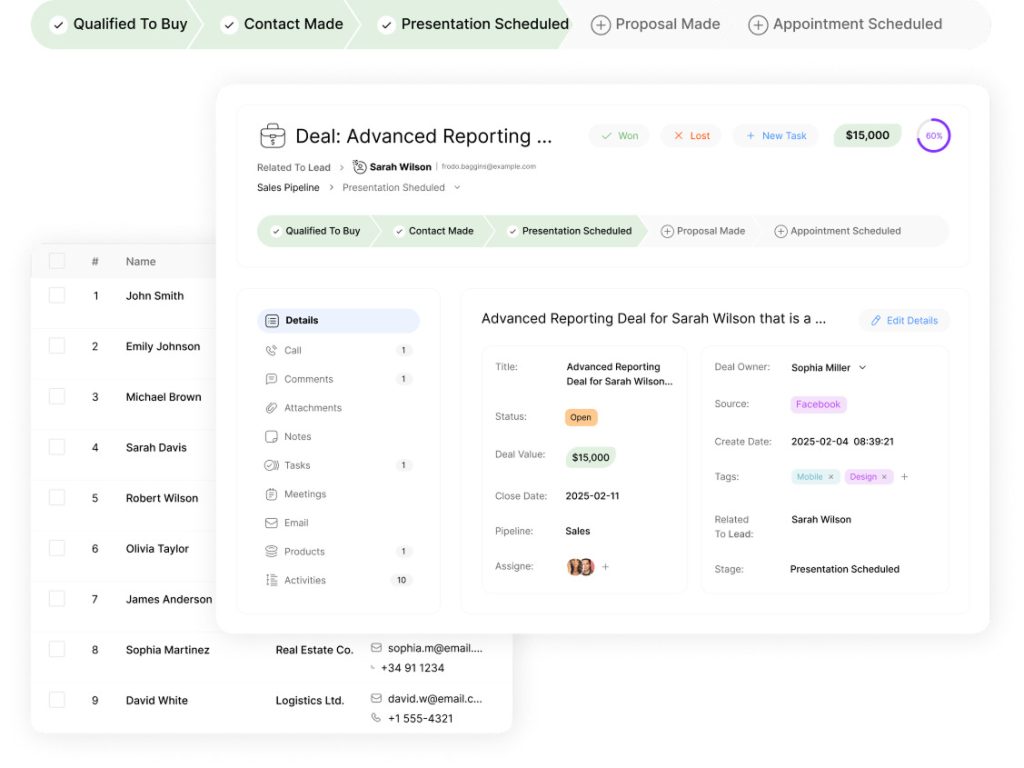
Are inefficient data-handling practices slowing your business growth? In today’s fast-paced business environment, the ability to manage deals and pipelines effectively is crucial for success with ClearCrm.
Efficient data import and export practices play a pivotal role in streamlining business operations, enabling companies to make informed decisions, reduce manual errors, and enhance customer relationships.
Mastering data transfer can significantly improve pipeline management, driving revenue and sustainable growth.
Key Takeaways
- Discover how effective data management can transform your deal management processes.
- Learn practical frameworks for configuring and optimizing data transfer systems.
- Understand how to reduce manual data entry and minimize errors.
- Explore strategies for creating more efficient workflows for your sales teams.
- Find actionable solutions to common challenges in deal data management.
Understanding the Role of Data Management in Deal Pipelines

In today’s business landscape, data management plays a pivotal role in driving deal pipeline success. Effective data management is not just about handling data; it’s about transforming it into a strategic asset that drives business growth.
How Data Flows Impact Business Growth
The flow of data within an organization significantly impacts its ability to grow and expand. When data is managed efficiently, it enables businesses to make informed decisions, reduce administrative costs, and accelerate deal cycles. To achieve this, using Unicode for data import and export is recommended, as it ensures consistency and eliminates potential failures due to Unicode characters. This is particularly important when configuring source data formats and establishing data mapping protocols.
To import or export data effectively, selecting a Unicode encoding ANSI code page as the Code page in the Regional settings tab is crucial. This simple step significantly improves data management reliability.
Key Benefits of Streamlined Data Management
Streamlined data management offers numerous benefits, including:
- Measurable ROI through reduced administrative costs, faster deal cycles, and improved customer retention rates.
- Up to 40% reduction in time spent on manual data entry and manipulation for organizations implementing structured data import/export processes.
- Accurate and accessible pipeline data enables sales managers to identify bottlenecks early and reallocate resources to high-potential opportunities.
- Standardized data formats and transfer protocols minimize integration challenges when adopting new tools or technologies.
- Automated data validation during import processes reduces error rates by up to 90% compared to manual data entry methods.
- Consistent data management practices create audit trails that support compliance requirements and simplify due diligence during growth phases or acquisition discussions.
- Sales teams with immediate access to complete customer data report higher confidence levels and improved performance metrics across the board.
- The ability to quickly generate custom reports from exported data enables more responsive strategic adjustments to changing market conditions.
By understanding the role of data management in deal pipelines, businesses can unlock these benefits and drive growth through more efficient and effective data handling practices.
The Fundamentals of Data Import & Export
Understanding the fundamentals of data import and export is crucial for effective deal pipeline management. Businesses rely on the smooth transfer of data to make informed decisions and drive growth.

Common Data Formats and Their Applications
Data import and export involve various file formats, each with its own applications. Common data formats include CSV, Excel, and XML. The choice of file format depends on the specific requirements of the business and the systems involved.
CSV files are widely used for data import and export due to their simplicity and compatibility with most systems. Excel files offer more advanced features, such as formatting and formulas, making them suitable for complex data analysis.
XML files provide a structured format for data exchange, allowing for the transfer of complex data sets between different systems.
Preparing Your Business Data for Transfer
Thorough data preparation is essential to ensure smooth data transfer operations. This involves several key steps:
- Conduct a comprehensive data audit to identify inconsistencies, duplicates, and gaps in the data.
- Standardize contact information, company names, and deal stage terminology to ensure consistent reporting and analysis.
- Implement data validation rules to flag potential issues before they enter the pipeline management system.
- Develop a data dictionary documenting field definitions, accepted values, and business rules.
- Establish clear data ownership and governance processes to define who can modify, approve, and transfer different types of pipeline information.
- Develop a systematic approach to handling special characters, formatting inconsistencies, and language variations.
- Consider implementing data enrichment processes to add value to basic contact and company information.
By following these steps, businesses can significantly reduce errors and improve the efficiency of their pipeline management processes. Implementing strategies for lead default management is essential, as it allows businesses to address potential issues before they escalate. Additionally, leveraging automation tools can streamline repetitive tasks, freeing up valuable time for teams to focus on nurturing leads and closing deals. This comprehensive approach not only ensures smoother operations but also enhances overall customer satisfaction.
For import projects, the option to truncate records in entities prior to import is available. This setting is off by default but can be useful for importing records into a clean set of tables. Mapping is a critical function that applies to both import and export jobs, determining which columns in the source file become the columns in the staging table.
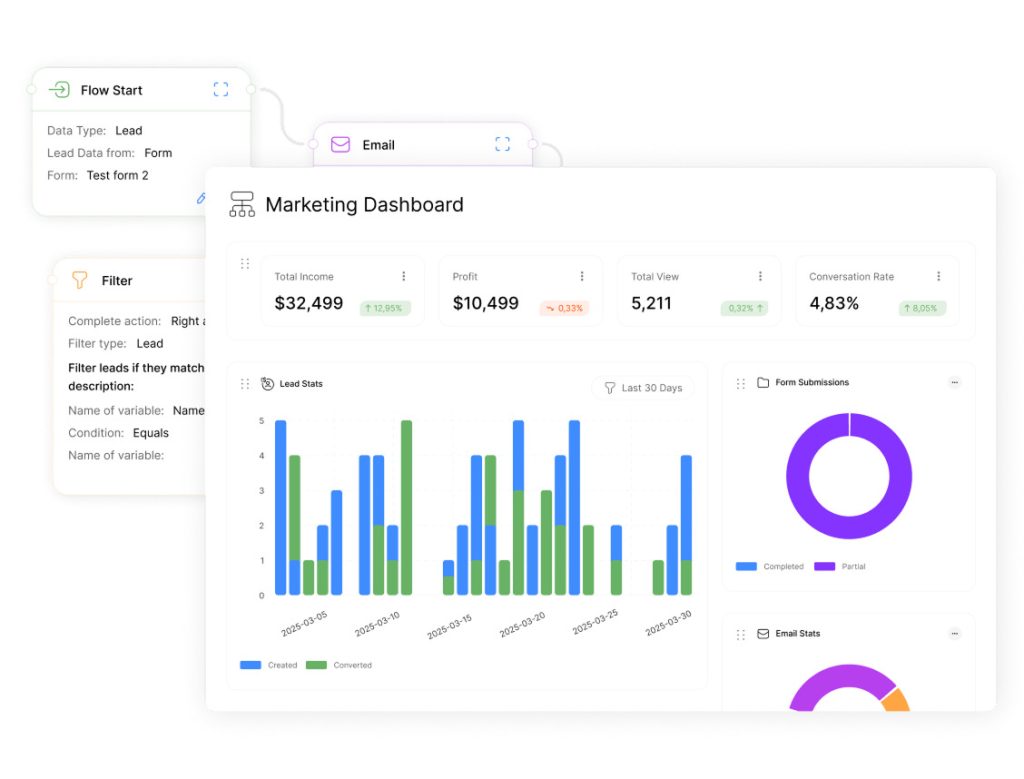
Setting Up Your Data Import & Export Framework
A well-configured data import and export framework is the backbone of efficient deal pipeline management. This framework enables businesses to seamlessly transfer data between systems, ensuring that information remains consistent and up-to-date across all platforms.
Configuring Source Data Formats
Configuring the source data format is a critical step in the data import process. The system relies on accurately formatted data to ensure smooth transitions between different data entities. When preparing your data for import, it’s essential to adhere to the required file format specifications to avoid compatibility issues.
The import tool is designed to handle various data formats, but it’s crucial to verify that your data is correctly formatted before initiating the import process. This includes ensuring that the data is free from errors and that all required fields are properly mapped.
To configure the source data format effectively:
- Identify the data format required by your import tool.
- Verify that your data is correctly formatted and free from errors.
- Map all required fields to their corresponding entities.
Establishing Data Mapping Protocols
Data mapping protocols are essential for maintaining data integrity during the import and export processes. When the column names in the staging table and the file match, the system automatically establishes the mapping based on the names. However, if the names differ, manual intervention is required to complete the mapping.
To establish effective data mapping protocols:
- Create a comprehensive inventory of all fields in both source and destination systems.
- Document data types, field lengths, and business definitions to ensure clarity.
- Identify primary keys and relationship fields that maintain connections between different data entities.
- Develop clear rules for handling data transformations, including date formatting and currency conversions.
- Establish protocols for managing required versus optional fields, including default values and validation rules.
By following these guidelines and configuring your data import and export framework correctly, you can ensure that your deal pipeline data is accurately transferred and maintained, supporting your business operations and decision-making processes.
Step-by-Step Guide to Importing Deal Data
Effective deal pipeline management begins with the accurate import of deal data. To achieve this, it’s crucial to understand the steps involved in importing business deal data into your management system.
Creating and Configuring Import Jobs
Creating and configuring import jobs is the first step in the data import process. This involves defining the source data file and configuring the import settings to match your business requirements. When setting up an import job, you need to specify the data format and map the data fields to the corresponding columns in your pipeline management system.
The configuration process includes selecting the appropriate data import settings, such as default values and data transformation rules. By carefully configuring these settings, you can ensure that your data is imported accurately and consistently.
Validating and Troubleshooting Import Processes
Once the import job is configured, it’s essential to validate and troubleshoot the import process to ensure data integrity. Check execution logs to identify errors or inconsistencies in imported data.
Thorough validation and effective troubleshooting processes are critical for maintaining data integrity and ensuring successful imports into your pipeline management system. Some best practices include:
- Implementing a multi-stage validation approach that includes pre-import data quality checks, in-process validation, and post-import verification.
- Developing clear error classification systems to distinguish between critical failures and minor issues.
- Creating comprehensive logging mechanisms to capture detailed information about each step of the import process.
- Establishing notification protocols to alert team members when validation failures or import errors occur.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your data import processes are reliable, efficient, and accurate, ultimately supporting effective deal pipeline management.
Mastering Data Export for Pipeline Analysis

To analyze pipeline performance effectively, mastering data export is crucial. Businesses can export contacts or accounts using the export tool available from Audience > Tools > Data Export and Import. This tool allows users to export all contacts or specific segments and contact lists, with the option to download the export file or store it on their own SFTP server.
Designing Effective Export Jobs
Designing effective export jobs is critical for obtaining relevant data for pipeline analysis. To achieve this, businesses should begin by establishing clear objectives for what they want to achieve with their exported data. This involves selecting the right data fields, configuring the export format, and determining the frequency of the export. By doing so, businesses can ensure that their exported data is accurate, comprehensive, and relevant to their analytical needs.
The export process can be optimized by leveraging the export tool’s capabilities, such as exporting all contacts or specific segments. This flexibility allows businesses to tailor their export jobs to their specific requirements, ensuring that they obtain the most valuable data for their pipeline analysis.
Leveraging Exported Data for Business Insights
Exported pipeline data becomes truly valuable when transformed into actionable business insights that drive strategic decisions and operational improvements. To achieve this, businesses should establish clear analytical frameworks that connect exported data to specific business questions about their pipeline performance and health.
- Implement visualization tools and techniques to transform raw exported data into intuitive dashboards and reports.
- Develop standardized analytical models to measure key pipeline metrics such as conversion rates, velocity, and value.
- Create collaborative analysis processes that bring together perspectives from sales, marketing, finance, and product teams.
- Establish feedback mechanisms to capture insights from data analysis and translate them into specific action plans.
By leveraging exported data effectively, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their pipeline dynamics and make informed decisions to optimize their strategies.
Optimizing Data Transfer Performance
Effective data transfer performance is vital for maintaining data integrity across pipeline management systems. To achieve this, businesses must focus on optimizing their data import and export processes.
Parallel Processing Techniques
One way to optimize data transfer performance is by utilizing parallel processing techniques. When executing a job that contains multiple data entities, entities without functional dependencies can be scheduled for parallel import or export. This significantly reduces the overall processing time and enhances efficiency.
To implement parallel processing, businesses can configure execution units that group related entities together. This allows independent data sets to be processed in parallel while maintaining sequential processing where dependencies exist. For example, entities with the same level can be processed in parallel, improving overall data transfer performance.
| Execution Unit | Level | Entity | Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | Entity A | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | Entity B | 2 |
| 2 | 2 | Entity C | 1 |
Sequencing Entities for Maximum Efficiency
Strategic sequencing of data entities is essential for maximizing transfer efficiency while maintaining data integrity. To achieve this, businesses should begin by mapping the dependencies between different data entities in their pipeline ecosystem.
- Develop a comprehensive entity relationship diagram to visualize the connections between different data types.
- Configure execution units that group related entities together, allowing independent data sets to be processed in parallel.
- Implement level-based processing within execution units to ensure that foundation data is established before dependent records are processed.
By establishing sequence numbering within levels, businesses can fine-tune the processing order of entities with similar dependency characteristics. This ensures that data is exported or imported in the correct order, maintaining data integrity throughout the process.
For instance, when importing deal data, entities can be sequenced in a data template or in import jobs. The execution unit, level, and sequence of an entity help control the order in which data is imported. By correctly sequencing entities, businesses can avoid errors and ensure a smooth data transfer process.
Securing Your Data During Import and Export

As businesses increasingly rely on data import and export, ensuring the security of these processes becomes paramount. Strong data security measures protect business data and maintain customer and stakeholder trust.
Role-Based Access Controls
Implementing role-based access controls is a critical step in securing data during import and export. By assigning access based on roles, organizations can ensure that sensitive data is only accessible to authorized personnel. This approach helps in reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized data modifications.
To configure role-based access controls effectively, consider the following:
- Identify the roles within your organization that require access to data import and export processes.
- Assign permissions based on the principle of least privilege, ensuring that users have only the necessary access to perform their tasks.
- Regularly review and update role assignments to reflect changes in personnel and organizational structure.
By using role-based access controls, organizations can enhance data security and comply with regulatory requirements. For instance, access to sensitive data fields can be restricted to specific roles, reducing the risk of data exposure.
| Role | Permissions | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Data Administrator | Full Access | Responsible for managing data import and export processes. |
| Data Analyst | Read-Only | Analyzes data for business insights. |
| Data Operator | Limited Access | Performs data import and export tasks under supervision. |
Legal Entity Considerations for Multi-Division Businesses
Multi-division businesses face unique challenges in managing data across different legal entities while maintaining appropriate security boundaries. To address these challenges, it’s essential to configure legal entity-based access controls on data jobs.
Consider the following best practices for managing data across legal entities:
- Map your organizational structure to understand the relationships between different legal entities.
- Develop clear policies regarding cross-entity data visibility and access.
- Implement data segregation in transfer processes to ensure information from different legal entities remains isolated when required.
By implementing these measures, organizations can ensure that data is handled appropriately across different legal entities, maintaining both security and compliance.
| Legal Entity | Data Access | Restrictions |
|---|---|---|
| Entity A | Full Access | None |
| Entity B | Limited Access | Restricted to specific data fields |
| Entity C | Read-Only | Access limited to viewing data |
Automating Data Workflows for Continuous Pipeline Management
Automating data import and export workflows is essential for maintaining a streamlined pipeline. By leveraging automation, businesses can ensure that their data workflows are efficient, reliable, and scalable.
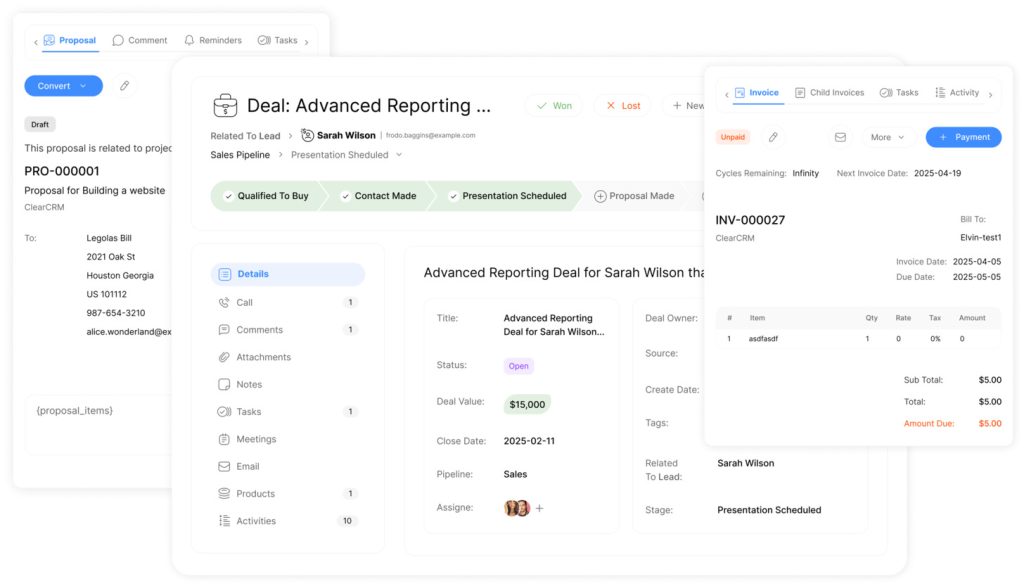
To achieve automation, businesses can schedule recurring data jobs and implement job history cleanup and archival processes. This not only improves system performance but also ensures compliance with data retention policies.
Scheduling Recurring Data Jobs
Scheduling recurring data jobs is a critical aspect of automating data workflows. By configuring jobs to run at regular intervals, businesses can ensure that their data is up-to-date and consistent. When scheduling data jobs, it’s essential to consider factors such as data volume, processing time, and dependencies between jobs.
For example, a business can schedule a daily data import job to retrieve new data from a source system, followed by a data export job to transfer the processed data to a target system. By automating these workflows, businesses can reduce manual errors and improve overall efficiency.
Implementing Job History Cleanup and Archival
Implementing effective job history cleanup and archival processes is crucial for maintaining system performance while preserving important historical data. Businesses should develop a comprehensive data retention policy that balances operational needs, analytical requirements, and compliance obligations.
- Establish tiered retention schedules to keep recent job history readily accessible while moving older information to cost-effective archival storage.
- Implement automated cleanup processes to regularly remove unnecessary history data according to retention policies.
- Create archival workflows to preserve important historical information in compressed, searchable formats.
- Develop restoration procedures to enable quick retrieval of archived data when needed.
- Implement appropriate security controls for archived data to ensure sensitive information remains protected.
- Establish monitoring mechanisms to verify the successful execution of cleanup and archival processes.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can ensure that their data workflows are automated, efficient, and compliant with regulatory requirements. This enables them to focus on higher-value activities and drive business growth.
Conclusion: Transforming Deal Management Through Effective Data Practices
Effective data practices revolutionize deal management by transforming it into a strategic function that drives business growth. By implementing the frameworks and techniques outlined in this guide, organizations can experience significant improvements in pipeline visibility, forecast accuracy, and deal velocity. Moreover, leveraging advanced analytics and data-driven insights allows teams to make informed decisions, minimizing risks and maximizing potential outcomes. By adopting effective lead management strategies for success, companies can ensure that their sales efforts align more closely with customer needs, facilitating smoother transactions and stronger relationships. Ultimately, the integration of these practices is essential for not only maintaining competitiveness but also for fostering long-term, sustainable growth. Additionally, the ability to implement custom sales stages visualization allows teams to tailor their processes specifically to the unique characteristics of their sales cycles. This personalization enhances clarity and focus, ensuring that each opportunity is tracked and nurtured effectively. By combining these visual tools with data-driven strategies, organizations can better identify bottlenecks and optimize their sales funnels for improved performance.
Key benefits of effective data management include:
- 30-50% improvements in pipeline visibility, forecast accuracy, and deal velocity
- Freedom from manual data handling, allowing sales and operations teams to focus on strategic activities
- A foundation for advanced analytics and AI applications that can identify patterns and predict outcomes
- A significant competitive advantage through faster response times and more personalized customer interactions
By mastering data import and export practices, businesses can ensure that their data is accurate, up-to-date, and accessible. This enables them to make informed decisions, drive business growth, and stay ahead of the competition. As organizations grow, the scalable approaches outlined in this guide will continue to support their evolving pipeline management needs. Furthermore, integrating the right tools for data management can significantly enhance the efficiency of the data handling processes. A top pipeline marketing software overview will provide insights into the best solutions available, allowing businesses to choose platforms that align with their specific requirements. Ultimately, leveraging these technologies will equip organizations to adapt swiftly to market changes and capitalize on new opportunities.
Effective data practices are essential for success in today’s fast-paced environment. By implementing these practices, organizations can leverage their data to drive continuous improvement in deal management and achieve sustainable business growth.

