Bulk Record Updates: A Step-by-Step Guide

Efficient data management is crucial for streamlining operations and enhancing customer relationships. One key aspect of this is performing bulk updates to records in a database or system.
Updating multiple records simultaneously can be a daunting task, but with the right approach, it can be done efficiently. This guide will walk you through the process, exploring the fundamental concepts and methods that enable effective updates.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have the knowledge to implement bulk record updates in your own applications, saving significant time and reducing manual effort.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the importance of bulk record updates in streamlining data management processes.
- Learn different methods and functions for effective bulk updates.
- Discover practical examples for handling various scenarios, from simple status updates to complex data transformations.
- Gain the knowledge to implement bulk record updates in your own applications.
- Reduce manual effort and save significant time.
Understanding Bulk Record Updates
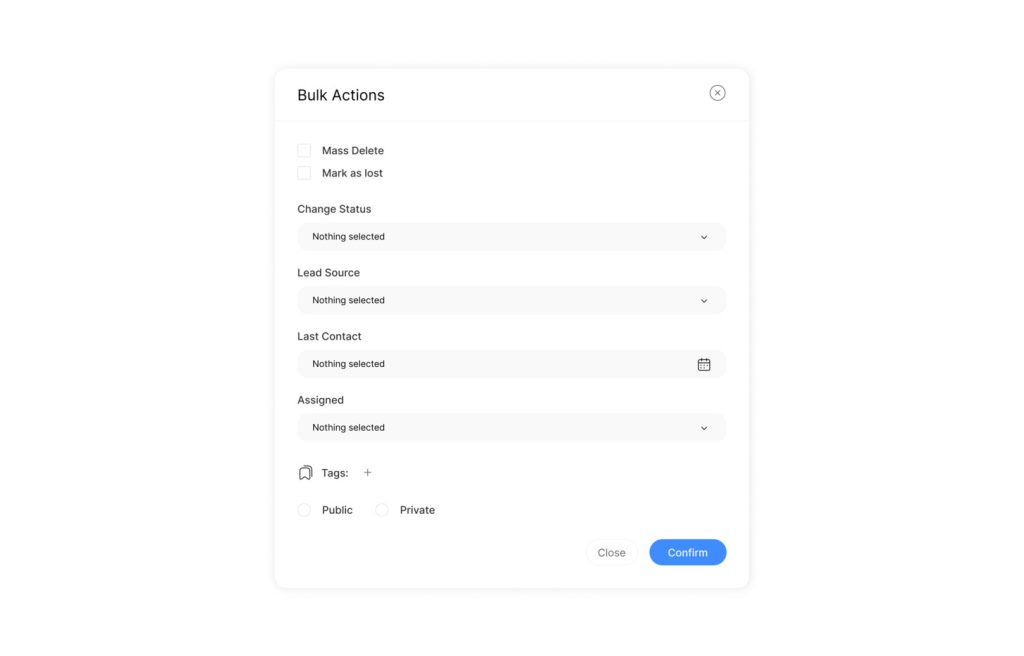
Bulk record updates are a crucial feature for managing large datasets efficiently. This capability allows businesses to modify multiple records simultaneously, streamlining data management processes.
What Are Bulk Record Updates?
Bulk record updates refer to the process of modifying multiple database records at once, rather than updating them individually. This approach significantly improves efficiency, especially when dealing with large datasets. By updating records in bulk, organizations can maintain data integrity and reduce the time spent on data management tasks.
Common Scenarios for Bulk Updates
There are several scenarios where bulk updates are particularly useful. For instance, when a company needs to update product prices across multiple regions or change customer information in bulk. Another example is when uploading multiple images or submitting a time sheet with a week’s worth of data at once. Bulk updates enable organizations to handle such tasks efficiently, saving time and reducing the likelihood of errors.
| Scenario | Benefit of Bulk Update |
|---|---|
| Updating product prices | Maintains consistency across regions |
| Changing customer information | Ensures data accuracy and reduces manual effort |
| Uploading multiple images | Streamlines data entry and reduces processing time |
By leveraging bulk record updates, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and improve data management. As noted by industry experts, “Bulk updates are a game-changer for companies dealing with large volumes of data, enabling them to make widespread changes quickly and accurately.”
“The ability to update records in bulk is a key component of effective data management systems.”
Preparing for Bulk Record Updates
Effective preparation is key to successful bulk record updates, ensuring data integrity and minimizing potential risks. Proper preparation involves several critical steps that help ensure a smooth and successful data update process.
Identifying Records That Need Updates
To update records efficiently, you must first identify which records require changes. This involves using filters, reports, and search functions to create targeted record sets. By doing so, you can ensure that your updates are applied to the correct data, reducing the risk of errors.
Organizing Your Data Structure
A well-organized data structure is essential for smooth bulk operations. This includes standardizing field formats and validating data consistency across your records. By organizing your data effectively, you can simplify the update process and minimize potential issues.
Creating Backup Before Making Changes
Before initiating any bulk changes, it’s crucial to create a comprehensive backup of your data. This protects your organization from potential data loss and ensures that you can recover your data in case something goes wrong during the update process.
Methods for Performing Bulk Record Updates
Effective bulk record updates rely on selecting the appropriate method that aligns with the specific requirements of the data sources involved. The choice of method depends on whether the data collection matches the structure of the target data source or if there are discrepancies that need to be addressed.
Using Patch() Function for Matching Data Sources
The Patch() function is ideal for scenarios where the data collection matches the structure of the target data source. It allows for straightforward updates by directly mapping the collection to the data source. For example, Patch(DataSource, Collection) updates records in the data source with the corresponding records from the collection.
Implementing ForAll() Function with Nested Patch
When data sources have different column structures, the ForAll() function combined with nested Patch operations provides a powerful solution. This approach enables complex updates by joining data sources based on common identifiers. An example is ForAll(Collection, Patch(DataSource, LookUp(DataSource, Id = Collection[@Id]), { Column: Value } ) ), which updates the data source by matching records from the collection.
Utilizing AddColumns() Function for Reference Lookups
The AddColumns() function is useful when the collection doesn’t have fields that directly map to the target table. It allows for creating reference lookups by adding columns to the collection that can be used to reference the data source. This method enhances flexibility in handling different data structures.
Step-by-Step Bulk Update Process

Managing bulk record updates can be simplified by breaking down the process into manageable steps. This section provides a detailed walkthrough of the complete bulk update process from initial setup to execution.
Setting Up Your Data Collections
To begin the bulk update process, it’s essential to set up your data collections properly. This involves structuring your source data for optimal processing. Ensure that your data is organized, and the necessary fields are identified for the update process.
Handling Columns with the Same Names
If your source and destination tables have the same column names, you can use a straightforward Patch statement for efficient updates. For example, if ChecklistItemsSource and the CheckedItems collections have the same column names, you can update the source at once with all the changes using the formula: Patch(ChecklistItemsSource, CheckedItems).
Managing Columns with Different Names
When the columns in your source and destination tables vary, you’ll need to use ForAll with Patch instead. This requires looping through each record using a condition that compares similar columns (e.g., Id column) between the different tables. This approach allows for more flexibility in managing updates across disparate data structures.
Bulk Creating New Records
You may want to create new records in bulk if, for example, you need to upload many images at once. The formula for bulk creating new records involves using ForAll with Patch, where you specify the defaults for the destination table and map the relevant fields from your source data. An example formula is: ForAll(NewChecklistItems, Patch(ChecklistItemsSource, Defaults(ChecklistItemsSource), {Id: Id, Category: Category, Description: Description, Status: Status})).
| Operation | Description | Example Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Update Same Column Names | Use Patch for same column names | Patch(ChecklistItemsSource, CheckedItems) |
| Update Different Column Names | Use ForAll with Patch | ForAll(CheckedItems, Patch(ChecklistItemsSource, LookUp(ChecklistItemsSource, Id = CheckedItems[@Id])))) |
| Create New Records | Use ForAll with Patch and Defaults | ForAll(NewChecklistItems, Patch(ChecklistItemsSource, Defaults(ChecklistItemsSource), {Id: Id, Category: Category, Description: Description, Status: Status})) |
Conclusion
By leveraging bulk record updates, organizations can achieve substantial improvements in data management efficiency. This guide has covered the essential techniques and methods for performing bulk updates, including preparation, data structuring, and the use of various functions like Patch() and ForAll().
Proper preparation is critical before performing bulk updates, including backing up your data and testing your updates to ensure accuracy. The different methods available for bulk updates offer flexibility based on your specific data structure and requirements.
Mastering bulk record updates can significantly enhance your data management capabilities, saving time and reducing errors. For further learning, explore additional resources on advanced bulk update techniques and related data management concepts.
Start implementing these practices in your own systems with small-scale updates before progressing to more complex scenarios, and you’ll be on your way to more efficient data management.

