How to Use Custom Task Statuses for Efficient Task Management
Traditional to-do lists often fail to capture the complexity of modern workflows. By implementing tailored progress indicators, teams gain precision in tracking work from initiation to completion. These visual markers do more than show where things stand – they align actions with business priorities and create accountability across departments. Additionally, integrating features like streamlining tasks with attachments can enhance collaboration, ensuring that all team members have access to relevant resources at their fingertips. This holistic approach fosters a more organized workflow and minimizes bottlenecks, as essential documents and updates are easily accessible. Ultimately, the combination of tailored progress indicators and streamlined task management promotes a more efficient and transparent work environment.
Sophisticated platforms allow organizations to define stages using color codes, scheduling rules, and clear ownership markers. For example, an Active label might trigger deadline calculations, while On Hold pauses timelines until blockers resolve. This dynamic approach prevents miscommunication about what needs attention now versus later.
Leaders using these systems report 23% faster project delivery times according to recent industry surveys. Real-time visibility into bottlenecks helps teams reallocate resources before delays escalate. Status-driven dashboards also transform individual updates into strategic insights about departmental performance.
Key Takeaways
- Tailored workflow stages mirror actual business processes better than generic lists
- Color-coded status updates reduce meeting time by 40% through instant clarity
- Automated scheduling rules prevent deadline overlaps in complex projects
- Executive reports convert task data into ROI-focused performance metrics
- Cross-department handoffs improve when stages define exact handover requirements
- Compliance-ready frameworks adapt to healthcare, finance, or legal workflows
Understanding Custom Task Statuses and Their Benefits
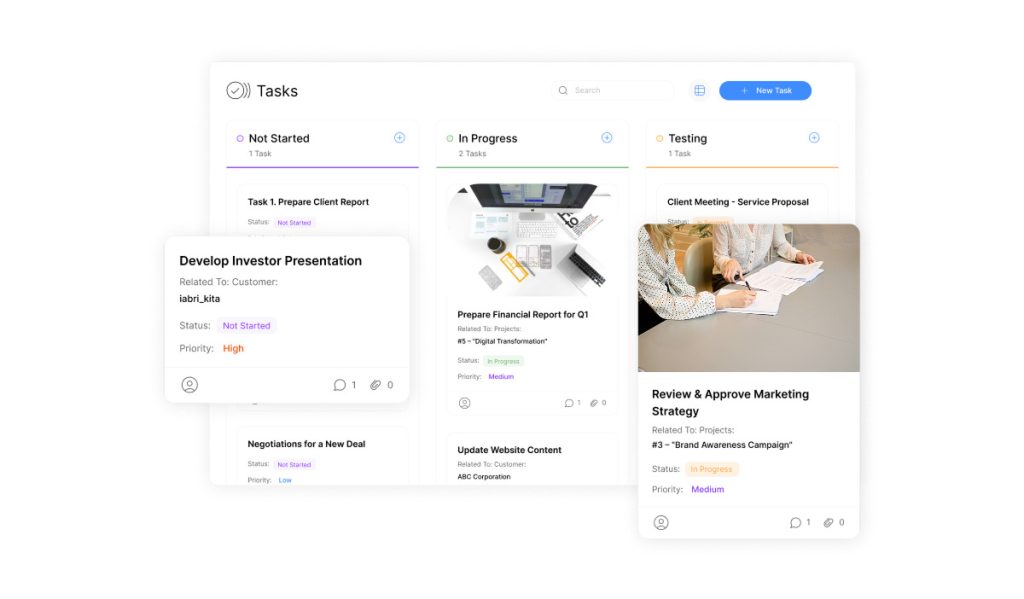
Modern workflows demand precision that generic labels can’t provide. Tailored progress indicators bridge this gap by mapping tasks to real-world processes. Teams configure stages like “Client Review” or “Awaiting Sign-Off” to mirror how work actually moves through departments.
Defining Progress Markers
Every status falls into one of four foundational types: Not Started (gray), Started (green), Needs Info (red), and Completed (blue). These default categories anchor more specific stages. For example, a marketing team might add “Copy Edits Pending” under Started or “Legal Approval Required” within Needs Info.
“Granular statuses cut our status update meetings by half,” notes a project manager at a tech firm. “Red labels immediately show where attention’s needed.”
Lifecycle Management Advantages
Color-coded systems enable instant workflow analysis. A dashboard dominated by red flags indicates systemic bottlenecks. Green-dominated views reveal smooth operations. This visual shorthand helps teams prioritize without sifting through descriptions.
Standardized terminology prevents confusion between departments. When engineering marks something “Ready for QA,” quality teams know exactly what’s required. Such clarity reduces duplicate work and accelerates handoffs.
Audit trails automatically form as tasks move through predefined stages. Financial institutions use this feature to demonstrate regulatory compliance. Healthcare teams track patient record reviews through verifiable status histories.
Setting Up and Managing Custom Task Statuses
Effective workflow management requires precise control over progress tracking systems. Authorized personnel streamline operations through centralized configuration tools designed for rapid deployment. These tools not only enhance visibility but also facilitate data-driven decision-making. By leveraging automation and real-time reporting, organizations can identify bottlenecks and allocate resources more efficiently, ultimately aiming to streamline your workflow effectively. As a result, teams can focus on their core objectives, driving productivity and improving overall performance.
Accessing Configuration Controls
Locate the gear icon in your platform’s left navigation menu. This gateway leads to administrative settings where Organization Administrators and Workspace Managers define rules. Strict access protocols prevent unauthorized adjustments to existing workflows.
Building and Modifying Tracking Stages
Select Create New in the administration hub to design progress indicators. The interface guides users through:
- Naming conventions that reflect team terminology
- Color coding for instant visual recognition
- Positioning within workflow sequences
Drag-and-drop functionality arranges stages in logical order, mirroring actual project lifecycles. Archived entries remain visible for historical reference but disable new assignments.
“Our quality assurance team reduced setup time by 30% using bulk editing features,” reports a manufacturing operations director.
Ensuring System Integrity
Limit modifications to trained administrators through role-based permissions. Real-time updates propagate across all active projects instantly, requiring advance communication before structural changes. Most platforms support 50 distinct status sets, each containing 20 stages for complex initiatives.
Consistent naming across lists prevents confusion during cross-department collaborations. Regular audits verify alignment between digital markers and evolving business processes.
Integrating Custom Task Statuses into Your Workflow
Successful workflow integration begins by aligning digital tools with actual operational rhythms. Teams achieve peak efficiency when progress indicators mirror real-world decision points rather than forcing artificial checkpoints.
Designing Purpose-Driven Workflows
Map stages to critical transitions like budget approvals or client feedback cycles. A software development group might use “Code Review” and “User Testing” labels that match sprint cadences. This approach turns abstract workflows into actionable roadmaps.
Implementation specialists recommend:
- Identifying three to five pivotal transition points per project phase
- Using color gradients to show advancement through complex processes
- Establishing automated alerts for stage-specific deadlines
“Our design team cut revision cycles by 18% after matching statuses to client review patterns,” explains a product development lead.
Bulk application tools streamline updates across multiple initiatives. Marketing departments often apply standardized campaign development markers to 20+ projects simultaneously while retaining flexibility for unique client requirements.
Cross-department collaboration improves when stages define exact handover criteria. Legal and creative teams using shared approval gates report 27% fewer miscommunications during product launches.
Change management proves critical during transitions. Progressive rollouts with pilot groups help organizations refine configurations before enterprise-wide adoption. Training materials should demonstrate how new markers solve specific pain points rather than simply listing features.
Custom Task Statuses: Best Practices and Implementation Tips

Well-designed progress indicators transform chaotic workflows into streamlined processes. Organizations achieve peak efficiency when status sets align with operational rhythms while allowing flexibility for unexpected shifts.
Using Custom Task Status Sets Effectively
Balance clarity with depth by limiting each set to 15-18 stages. A software team might use “Code Review” and “QA Passed” instead of generic In Progress labels. Clear naming conventions prevent confusion – marketing and legal teams should interpret stages identically.
“We reduced project setup time by 40% after standardizing our status terminology,” shares a Fortune 500 operations lead.
Color-coding works best when tied to urgency levels. Reserve red for blockers requiring immediate action. Use analytics to retire rarely used stages – if “Design Revision” appears in under 5% of projects, consolidate it with broader categories.
Leveraging Integrations and Managing Changes
Platforms allowing 50 status sets per account enable tailored tracking for diverse projects. However, third-party tools might not recognize new labels. Test automated reports before full deployment to prevent data gaps.
Implement changes through three phases:
- Pilot revised sets with one department
- Document adoption rates and friction points
- Adjust configurations before enterprise rollout
Restrict editing rights to designated administrators through access groups. This prevents unauthorized modifications while letting managers apply pre-approved sets. Monthly audits ensure systems evolve with business needs without creating tool bloat.
Conclusion
Adopting tailored progress tracking systems elevates organizational efficiency beyond basic checklists. These frameworks convert routine updates into strategic insights, aligning team efforts with core business goals. Companies using dynamic labeling report measurable gains in project visibility and deadline adherence across departments. Moreover, integrating these systems with top time tracking solutions enhances accountability and promotes a culture of continuous improvement. By seamlessly capturing time spent on tasks, organizations can identify bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation. This not only drives productivity but also empowers teams to make informed decisions that propel projects forward.
By mapping workflows to real-world processes, teams create self-correcting systems that highlight bottlenecks before they escalate. Leaders who invest time in structured implementation see 19-35% faster delivery cycles according to industry benchmarks. Clear accountability structures emerge when every status change triggers automated notifications and historical records.
Continuous refinement keeps these tools aligned with evolving priorities. Regular reviews of task flow patterns help teams retire redundant stages and amplify high-impact markers. This approach transforms temporary fixes into lasting operational advantages.
The true power of progress tracking lies in its cultural impact. Organizations using these methods consistently demonstrate tighter resource allocation and stronger cross-team alignment. When implemented thoughtfully, these systems become catalysts for transparency and measurable growth across all project portfolios.

